Context:
- A team of scientists led by researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Gandhinagar, Gujarat, has developed a nanocomposite material that can selectively convert environmental carbon monoxide into less toxic carbon dioxide.
Carbon monoxide
- A major air pollutant that poses a serious threat to health.
The new composite material:
- Made of graphene and an alloy of platinum and palladium in the form of nanoparticles.
- In the project, graphene was used as a substrate and then “decorated” with alloy nanoparticles made of platinum and palladium.
- The novel catalytic structure was then used for selective oxidation of CO into CO2. The use of a metal particle of certain orientation which absorbs or interacts with CO at lower energy helped the conversion.
- The new material could find potential use in chemical industries as well as environmental cleaning, the researchers said.
- While the concept used is novel and important as CO is a major environmental problem, it may take a while for this science to be converted into technology because the experimental set-up appears complex and may not be commercially viable.
What is Graphene?
- Although carbon can form three-dimensional lattices by bonding with four other carbon atoms to form diamond, it can also form two-dimensional sheets (a sheet of paper has only two dimensions, for example) when it bonds to three other carbon atoms. These sheets are called graphene.
- Researchers have only recently (2004) been successful in producing sheets of graphene for research purposes, though they all probably had a handy form of graphene in their pocket protectors. Common graphite is the material in pencil lead, and it’s composed of sheets of graphene stacked together. The sheets of graphene in graphite have a space between each sheet, as illustrated in the following figure, and the sheets are held together by the electrostatic force called van der Waals bonding.
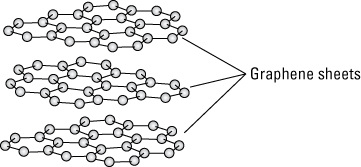
Sheets of graphene held together by van der Waals bonding make graphene.
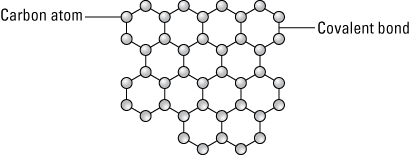
Graphene sheets are composed of carbon atoms linked in hexagonal shapes, as shown in the following figure, with each carbon atom covalently bonded to three other carbon atoms. Each sheet of graphene is only one atom thick and each graphene sheet is considered a single molecule. Graphene has the same structure of carbon atoms linked in hexagonal shapes to form carbon nanotubes, but graphene is flat rather than cylindrical.
How can nanotechnology reduce air pollution?
- There are two major ways in which nanotechnology is being used to reduce air pollution: catalysts, which are currently in use and constantly being improved upon; and nano-structured membranes, which are under development.
- Catalysts can be used to enable a chemical reaction (which changes one type of molecule to another) at lower temperatures or make the reaction more effective. Nanotechnology can improve the performance and cost of catalysts used to transform vapors escaping from cars or industrial plants into harmless gasses. That’s because catalysts made from nanoparticles have a greater surface area to interact with the reacting chemicals than catalysts made from larger particles. The larger surface area allows more chemicals to interact with the catalyst simultaneously, which makes the catalyst more effective.
- Nanostructured membranes, on the other hand, are being developed to separate carbon dioxide from industrial plant exhaust streams. The plan is to create a method that can be implemented in any power plant without expensive retrofitting.
Source:TH
