Context
-
The Peruvian government has recently declared a state of national emergency for up to three months, due to a spike in the number of cases of a rare neurological disorder called Guillain-Barré Syndrome .
-
The disorder, which affects the body’s nervous system, is characterized by muscle weakness and breathing difficulties, and can even lead to total paralysis in extreme situations.
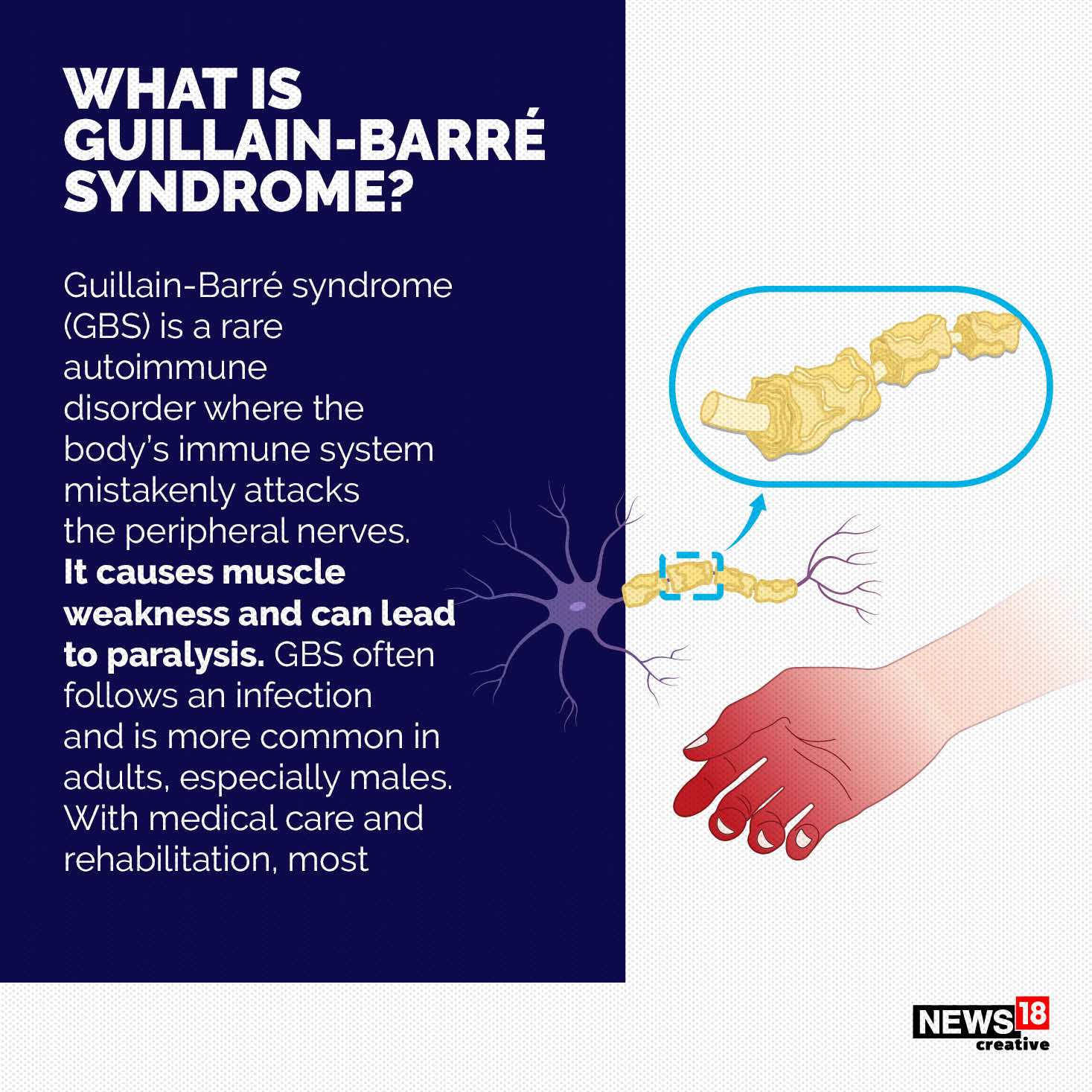
What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome is a rare neurological disorder where the body’s immune system which normally protects it from infections and other foreign bodies mistakenly attacks its own peripheral nerve cells.
- More specifically, the myelin sheath an insulating layer of fat and protein that surrounds the nerve cells becomes inflamed.
- The myelin sheath enables signals to pass through the nerve tracts at breakneck speed under normal conditions. If the sheath is inflamed, the nerves can hardly transport stimuli.
- Simply put, a person with this syndrome will have difficulty speaking, walking, swallowing, excreting or performing other normal functions of the body. The condition can get progressively worse. Thus, the peripheral nerves the nerves that branch out from the brain and the spinal cord get damaged as a result, and the muscles can become weak or paralyzed.
- The first symptoms include a tingling sensation in the body’s extremeties, weakness in the legs that spreads to the upper body, difficulty in facial movements, unsteady walking or inability to walk, pain and, in severe cases, paralysis.
What causes Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
- The exact reasons for Guillain-Barré Syndrome are not yet understood.
- However, it often develops shortly after a person gets an infectious disease.
- Rarely, vaccinations can cause it. Guillain-Barré Syndrome, or GBS, also was linked to the cytomegalovirus, Epstein Barr virus, Zika virus and even the COVID-19 pandemic.
Why does this happen?
- Scientists say that our immune system is highly specialized to recognize foreign substances such as viruses, bacteria and fungi.
- It produces proteins called antibodies that bind to the surface structures of pathogens while building up an immune response against them.
- In an autoimmune disease like Guillain-Barré Syndrome, the invaders camouflage themselves with a surface that mimics the body’s own structures.
Is Guillain-Barré Syndrome curable?
- The condition of the patient tends to worsen for up to two weeks after the onset of the disease.
- At week four, the symptoms plateau, after which recovery begins.
- The recovery can extend from anywhere between six to 12 months and occasionally up to three years.
- Currently, there is no certain cure for Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
- The paralysis not only affects the legs and arms, but also important parts of the nervous system that regulate breathing, blood pressure and heartbeat.
- To prevent this from happening, doctors continuously monitor the patient’s vital signs and, in case of an emergency, put them on a ventilator.
There are also two treatments that can help recovery and reduce the severity of the disease.
- The first is plasma exchange or plasmapheresis.
- The plasma or the liquid part of the blood is removed and separated from the blood cells, inducing new plasma production to make up for the loss. This treatment is aimed at removing the antibodies which are attacking the peripheral nerves.
- The second available therapy is called immunoglobin therapy, where healthy antibodies from blood donors are injected intravenously.
- The damaged antibodies contributing to GBS are then blocked by the high doses of the immunoglobulins.
- Apart from this, physical therapy might also be useful in alleviating pain.
Source: IE
Visit Abhiyan PEDIA (One of the Most Followed / Recommended) for UPSC Revisions: Click Here
IAS Abhiyan is now on Telegram: Click on the Below link to Join our Channels to stay Updated
IAS Abhiyan Official: Click Here to Join
For UPSC Mains Value Edition (Facts, Quotes, Best Practices, Case Studies): Click Here to Join
