Context
-
The US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) July report on global climate has said that, since 1880, the month of July 2021 is the hottest month on record.
-
A recent IPCC report had issued a strong warning about an impending climate crisis, attributing rising wildfires, heatwaves, extreme rainfall and floods to human activity.
Key Findings of the report
- The report advised deep cuts to CO2 emissions, failing which the rising temperatures will lead to permanent damage.
- Data show that July 2021 is the hottest month on record in the last 142 years for which data are available.
-
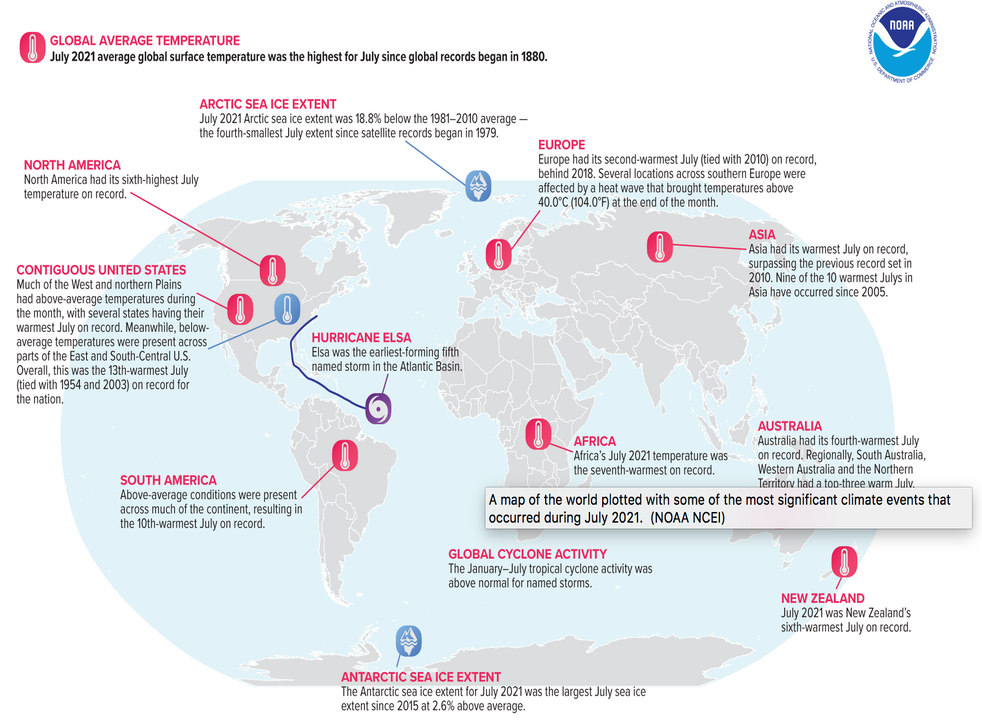
Source : The Independent - And the temperature rise is not limited to a region — every continent has recorded peak levels in the last 10 years.
- Asia recorded its warmest ever July in 2021.
July 2021 is the hottest month on record
- The global surface temperature in July 2021 was 0.93°C more than the 20th century (1901-2000) average of 15.8°C.
- It is the highest deviation from the average for any July in the past 142 years.
- In the Julys of 2016, 2019 and 2020, it had deviated to 0.92°C from the average.
- Nine of the 10 warmest Julys ever have been recorded since 2010.
- Significantly, seven of the warmest Julys have occurred since 2015.
Various scenarios
- If current policies continue, if all countries achieve their pledges for emissions reductions, and the necessary pathways which are compatible with limiting warming to 1.5°C or 2°C of warming this century.
- If all countries abandon their climate change policies, the global surface temperature is estimated to increase by 4.1-4.8°C by 2100 compared to pre-industrial levels.
- If current climate change policies continue as they are, the global surface temperature is estimated to increase by 2.7-3.1°C by 2100 compared to pre-industrial levels.
- If all countries adhere to Paris Agreement pledges and targets for emissions reductions, the global surface temperature is estimated to increase by 2.4°C by 2100 compared to pre-industrial levels.
Extreme temperatures
- The number of years in which extreme temperature events are projected to occur in a 10-year period under different global warming levels compared to the average temperature recorded between 1850-1900 without human influence.
- Each dot represents a year, and a darker dot depicts a year that could have higher than average temperatures.
- For instance, in the 1850-1900 period, one year on average in a decade recorded higher than average temperatures.
- Under current warming levels, nearly three years in a decade are likely to have high temperatures.
- If warming levels touch the 2°C mark, over five years in a 10-year period could have higher than normal temperatures.
Environment Current Affairs 2021 : Click Here
