Context
-
NITI Aayog released a comprehensive study on the not-for-profit hospital model in the country, in a step towards closing the information gap on such institutions and facilitating robust policymaking in this area.
Need for Not-for-Profit Hospital
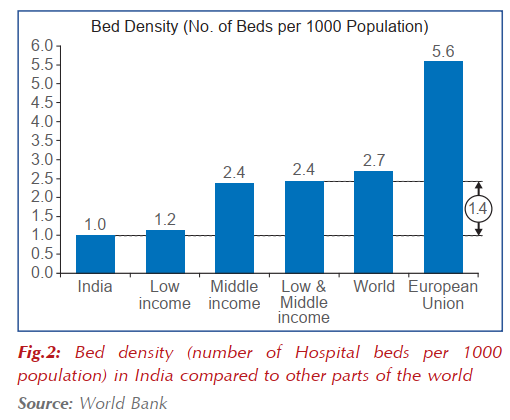
- Despite economic growth and modernization, India continues to face significant challenges of unavailability and unaffordability in healthcare services. This is substantiated by the fact that India has a lower Bed Density than the rest of the world.

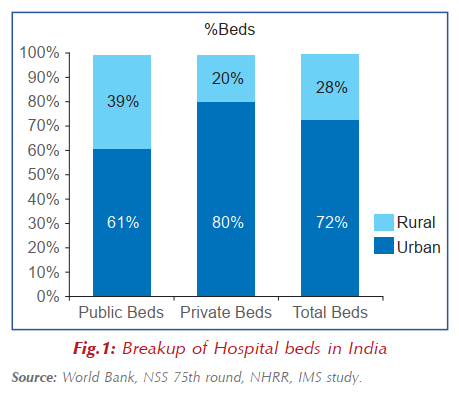
Source: TOI - In addition, existing hospital beds and hospitalization services have a high level of concentration in urban areas, which in turn impact the accessibility and affordability of hospitalization services.
- The not-for-profit hospitals currently account for only a miniscule share of hospitalization cases.
- Public hospitals that offer healthcare at negligible cost are overstretched. The burden of healthcare provision shifts to private hospitals, which generally offer healthcare at a higher cost to the patient, as they must sustain themselves.
- Private hospitals are largely divided into “for-profit hospitals,” which account for 23.3% of treated ailments and “not-for-profit hospitals,” which account for only 1.1% of treated ailments, as of June 2018.
- The disparity is further revealed in terms of hospitalization cases, wherein the for-profit hospitals account for 55.3% of in-patients, while the not-for-profit hospitals account for only 2.7% of in-patients in the country, according to the findings of the NSS 75th round survey on Health in India.
Key Facts on Bed Density and Hospital Beds in India
Operationalization of Not-for-Profit Hospital
- A not-for-profit hospital does not make profits for its owners from the funds collected for patient services.
- The owners of these hospitals are often charitable organizations or non-profit corporations.
- The fees for service at these hospitals are generally lower than for-profit hospitals and the income from fees (above the cost of service) are reinvested in the hospital.
- These hospitals are a potential remedy to the challenges of unavailability and unaffordability of healthcare in India.
- The infrastructure, services, and charges of these hospitals are positioned to cater to the unreached and underprivileged population of the country.
- In addition, these hospitals have managed to create a perception of goodwill in the country not only through selfless healthcare services with a social cause, but also through various community engagement programs for education, vocational training, hygiene, sanitation, women’s empowerment and employment.
Four categories were defined for the not-for-profit hospitals:
- Faith-based Hospitals
- Community-based Hospitals
- Cooperative Hospitals
- Private Trust Hospitals
Key Findings
- Most of the not-for-profit hospitals charge lower than the for profit hospitals.
- Most of the Not-for-profit Hospitals are empaneled with State or Central Government Healthcare schemes.
- The not-for-profit hospitals use various levers to facilitate their low cost of clinical care and reduced operational expenditure
- Not for profit Hospitals have lower operating costs as compared to For-Profit Hospitals
- A strong focus on quality care across all categories of not-for-profit hospitals, as most of them had some form of accreditation for their services
Challenges faced by not-for-profit hospitals
- Recruitment and retention of doctors & staff
- Reimbursements for treatment of Government health scheme beneficiaries
- Infrastructure and equipment expansions
- Regulatory challenges
- High compliance burden of staffing requirements of the Regulations for running a blood bank, Clinical Establishments Act, PNDT Act, and Quality standards.
Proposed Policy Interventions to Promote the Not-for-Profit Hospital Sector
SHORT TERM
- Identification and promotion
- Develop mechanisms to rank these hospitals on a performance index
- Create a national level portal/directory of these hospitals
- Leveraging expertise
- Representatives of high-performing not-for-profit hospitals across different geographical locations can be invited to share their experiences in relevant policymaking committees
- Human resources
- Representatives of high-performing not-for-profit hospitals across different geographical locations can be invited to share their experiences in relevant policymaking committees
- Financial
- 100% exemption for donations under section 80G
- Extension of a low-cost credit line (esp. working capital loans)
- Income-tax exemption for membership fees paid at Cooperative Trust Hospitals
- Single window clearance for Government reimbursements
LONG TERM
- Identification & Promotion
- Promote the top hospitals for facilitating philanthropy, investments and patient flows
- Leveraging of expertise
- Involving high performing Hospitals in PPP models for managing PHCs, operations of Government Facilities, PSU Hospitals
- Human resources
- Revisiting the compliance requirements of regulations such as CEA, PNDT, Blood Bank
- Develop a mechanism to incentivize super-specialists to work in remote areas
- Operations & Financial
- Grant-in-Aid scheme
- Timely allocation of unencumbered land
Source: https://niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2021-06/Not-for-profitHospitalReport.pdf
Social Justice Archives: Click Here