Context
-
In its first hike since 2018, the US Federal Reserve raised interest rates by 25 basis points and outlined an aggressive stance that also includes balance sheet reduction aimed at fighting record high inflation.
-
It also cited the war in Ukraine as creating additional upward pressure on inflation, with global commodity prices remaining elevated.
What impact has the Fed Reserve hike had on financial markets?
- Markets responded positively to the clear path outlined by the world’s largest central bank, with US markets closing higher by 2 per cent and Indian stock markets opening with a gap of more than 1 per cent.
- Commodities retreated with the Brent crude oil falling and remaining below $99 per barrel, sharply lower than the $139 per barrel recorded just a few days ago.
- Going forward, Indian and global markets are expected to stay positive as three major uncertainties seem to be over — the Assembly elections in five Indian states, the US Fed’s decision, and signs of the Russia-Ukraine conflict entering a resolution phase.
- Any spike in commodity prices could cause corrections in equity markets, even as the broader trend of rising stock prices remains intact.
How will it impact the RBI policy decision?
- The Fed’s decision to hike rates and rising domestic retail inflation rate will have a direct bearing on the Reserve Bank of India’s monetary policy review at the next meeting of the Monetary Policy Committee.
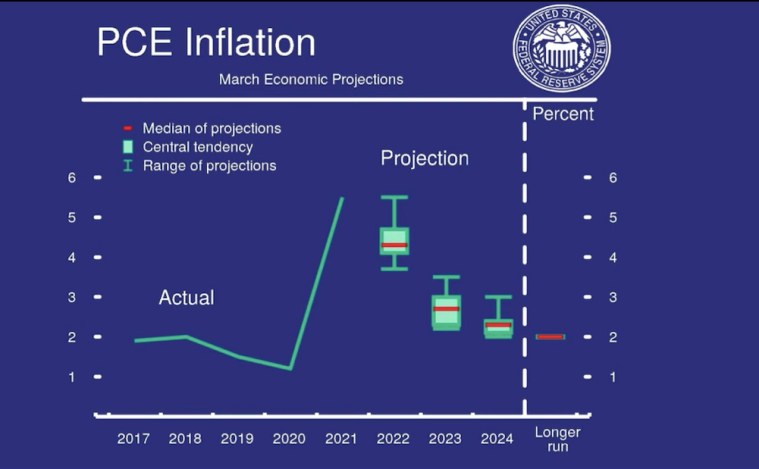
Chart source: US Fed - Unlike the US Fed, which has clearly reversed course from its accommodative monetary policy, the RBI continues to hold an accommodative stance. This is partly because the retail inflation in India has not breached the set target range of the RBI.
- As per recent data, domestic retail inflation rose to an eight month high in February 2022.
- Some economists argued that the RBI may have to revise upward its inflation forecast as inflationary pressures are becoming generalised.
- A reassessment of the current accommodative stance of the central bank is also possible. This is the fifth consecutive month of rising inflation.
What will be the breach of the RBI inflation target?
- According to the Finance Ministry, two months of over 6 per cent retail inflation cannot be seen as a breach of the upper band of RBI’s target, and crossing of the inflation rate above the 6 per cent band “for a particular month cannot be construed as breach of target”.
- Breach of this inflation target is construed only when:
- (a) the average inflation is more than the upper tolerance level of the inflation target for any three consecutive quarters; or
- (b) the average inflation is less than the lower tolerance level for any three consecutive quarters.
Back to Basics
The role of the Fed
- The US central bank system performs five broad functions to promote the effective operation of the American economy. The Federal Reserve identifies these functions as follows:
- conducting the US monetary policy to promote maximum employment and stable prices;
- promoting the stability of the financial system and seeking to minimize and contain systemic risks through active monitoring and engagement in America and overseas;
- promoting the safety and soundness of individual financial institutions and monitoring their impact on the financial system as a whole;
- fostering safety and efficiency in the payment and settlement system through services to banks and the federal government that facilitate US-dollar transactions and payments;
- promoting consumer protection and community development through consumer-focused supervision and examination, research and analysis of emerging consumer issues and trends, and the administration of consumer laws and regulations.
Monetary policy
- Monetary policy refers to actions taken by the Fed to influence the availability and cost of money and credit to help promote national economic goals. The Federal Reserve controls the three tools of monetary policy: open market operations, discount rate, and reserve requirements.
- The federal funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions lend balances at the Federal Reserve to other depository institutions overnight. Changes in the federal funds rate trigger a chain of events that affect other short-term interest rates, foreign exchange rates, long-term interest rates, the amount of money and credit, and, ultimately, a range of economic variables, including employment, output, and prices of goods and services
Reference
Visit Abhiyan PEDIA (One of the Most Followed / Recommended) for UPSC Revisions: Click Here
IAS Abhiyan is now on Telegram: Click on the Below link to Join our Channels to stay Updated
IAS Abhiyan Official: Click Here to Join
For UPSC Mains Value Edition (Facts, Quotes, Best Practices, Case Studies): Click Here to Join
