Context
-
After the Centre’s nod for creation of the Ramgarh Vishdhari sanctuary, the Rajasthan government is hoping to develop a tiger corridors connecting three tiger reserves passing through districts including Sawai Madhopur, Kota and Bundi.
Key Details about Ramgarh Tiger Reserve
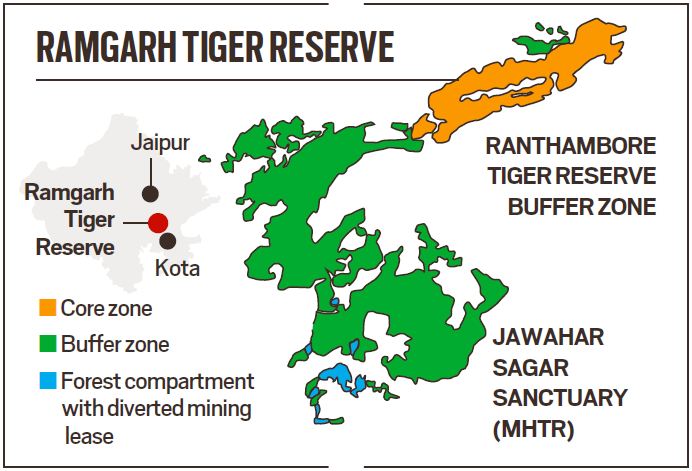
- The Ramgarh Vishdhari Sanctuary has been approved as 52nd Tiger Reserves of India and 4th Tiger Reserve of Rajasthan.
- According to a 2018 tiger census, there are 102 tigers in three reserves — Ranthambore Tiger Reserve in Sawai Madhopur, Sariska Tiger Reserve in Alwar, and Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve in Kota — in the state.
- The Ramgarh Tiger Reserve will link Ranthambore Tiger Reserve in the Northeast & Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve on the southern side.
- Tigers have always frequented the area demarked for the Ramgarh Vishdhari tiger sanctuary and even now, tigers regularly pass through this area from the direction of Ranthambore.
- It is adjoining the buffer area of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve. This newly proposed tiger reserve in Bundi district will connect the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve in Sawai Madhopur district with the Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve in Kota district.
- While the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve at present has a population of more than 65 tigers, the Mukundra reserve is presently left with just one big cat, after a series of deaths inside the reserve.
- To strengthen the prey base, the state has already approved shifting of chital (spotted deer) from Ghana Bird Sanctuary (Karauli) to Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve, Keoladeo National Park, and Ramgarh Vishdhari.
Tiger corridors in India
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority in collaboration with the Wildlife Institute of India has mapped out 32 major corridors across the country.
- These are operationalized through a Tiger Conservation Plan, mandated under section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
The list of macro/landscape level tiger corridors are as under:
| Landscape | Corridor | States/ Country |
| Shivalik Hills & Gangetic Plains | (i) Rajaji-Corbett | Uttarakhand |
| (ii) Corbett-Dudhwa | Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Nepal | |
| (iii) Dudhwa-Kishanpur Katerniaghat | Uttar Pradesh, Nepal | |
| Central India & Eastern Ghats | (i) Ranthambhore-Kuno-Madhav | Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan |
| (ii) Bandhavgarh-Achanakmar | Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh | |
| (iii) Bandhavgarh-Sanjay Dubri-Guru Ghasidas | Madhya Pradesh | |
| (iv) Guru Ghasidas-Palamau-Law along | Chhattisgarh & Jharkhand | |
| (v) Kanha-Achanakmar | Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh | |
| (vi) Kanha-Pench | Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra | |
| (vii) Pench-Satpura-Melghat | Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra | |
| (viii) Kanha-Navegaon Nagzira-Tadoba-Indravati | Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh | |
| (ix) Indravati-Udanti Sitanadi-Sunabeda | Chhattisgarh, Odisha | |
| (x) Similipal-Satkosia | Odisha | |
| (xi) Nagarjunasagar-Sri Venkateshwara National Park | Andhra Pradesh | |
| Western Ghats | (i) Sahyadri-Radhanagari-Goa | Maharashtra, Goa |
| (ii) Dandeli Anshi-Shravathi Valley | Karnataka | |
| (iii) Kudremukh-Bhadra | Karnataka | |
| (iv) Nagarahole-Pusphagiri-Talakavery | Karnataka | |
| (v) Nagarahole-Bandipur-Mudumalai-Wayanad | Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu | |
| (vi) Nagarahole-Mudumalai-Wayanad | Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu | |
| (vii) Parambikulam-Eranikulam-Indira Gandhi | Kerala, Tamil Nadu | |
| (viii) Kalakad Mundanthurai-Periyar | Kerala, Tamil Nadu | |
| North East | (i) Kaziranga-Itanagar WLS | Assam, Arunachal Pradesh |
| (ii) Kaziranga-Karbi Anglong | Assam | |
| (iii) Kaziranga-Nameri | Assam | |
| (iv) Kaziranga-Orang | Assam | |
| (v) Kaziranga-Papum Pane | Assam | |
| (vi) Manas-Buxa | Assam, West Bengal, Bhutan | |
| (vii) Pakke-Nameri-Sonai Rupai-Manas | Arunachal Pradesh, Assam | |
| (viii) Dibru Saikhowa-D’Ering-Mehaong | Assam, Arunachal Pradesh | |
| (ix) Kamlang-Kane-Tale Valley | Arunachal Pradesh | |
| (x) Buxa-Jaldapara | West Bengal |
Tiger Reserves in India : Click Here
