Context
-
The World Health Organization has classified a new variant of the novel coronavirus, which belongs to a lineage named B.1.1.529, as a ‘variant of concern’, and named is Omicron.
-
This variant was first identified by scientists in South Africa, but has spread to nearly a dozed countries including Australia, Italy, Germany, the Netherlands, Britain, Hong Kong, Botswana and Belgium.
So, what is different about Omicron and why is it deemed a high risk? Do vaccines work against it? What should you do? Take a look:

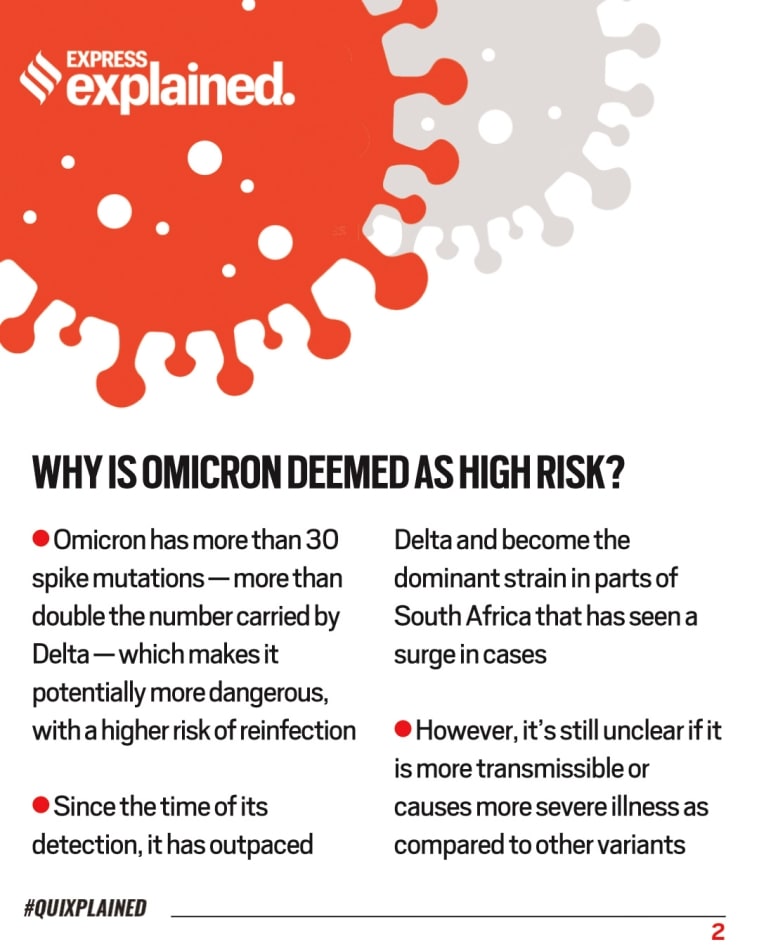


- The emergence of the new variant shows once again that the pandemic is far from over — and Covid-appropriate behaviour is critical for breaking the chain of transmission: masking, social distancing, good ventilation in all shared spaces, and washing or sanitising hands and surfaces regularly.
Newest variant of SARS-CoV-2
- In picking a name for the newest variant of SARS-CoV-2, Omicron, the World Health Organization (WHO) has skipped two letters of the Greek alphabet, one of which also happens to be a popular surname in China
- The WHO has been using Greek letters to refer to the most widely prevalent coronavirus variants, which otherwise carry long scientific names. It had already used 12 letters of the Greek alphabet before the newest variant emerged in South Africa
- The WHO said Nu could have been confused with the word ‘new’ while Xi was not picked up following a convention.
- All variants are given scientific names that represent their parentage and the chain of evolution. Omicron, for example, is also known by its more scientific designation B.1.1.529, which shows that it has evolved from the B.1 lineage.
- Since the scientific names are not easy to remember, the more prevalent variants started to be named after the country from where they were first reported: ‘UK variant’, ‘Indian variant’, ‘South African variant’, or ‘Brazilian variant’. To remove the connection with specific countries, which was triggering name-calling and blame game, the WHO decided on a new naming system using Greek letters.
- The variant that earlier used to be referred as the ‘Indian’ thus got the name Delta, while the one being associated with the UK was named Alpha.
WHAT IT MEANS
- As an infected cell builds new coronaviruses, it occasionally makes tiny copying errors. These called mutations. Mutations are passed down through a lineage, a branch of the viral family tree. A group of coronaviruses that share the same inherited set of distinctive mutations is called a variant.
VARIANTS OF CONCERN
The WHO currently lists 5 variants of concern:
- Omicron (B.1.1.529), identified in southern Africa in November 2021
- Delta (B.1.617.2), which emerged in India in late 2020 and spread around the world
- Gamma (P.1), which emerged in Brazil in late 2020
- Beta (B.1.351), which emerged in South Africa in early 2020
- Alpha (B.1.1.7), which merged in Britain in late 2020
- VARIANTS OF INTEREST
There are currently two:
- Mu (B.1.621), which emerged in Colombia in early 2021
- Lambda (C.37), which emerged in Peru in late 2020
Visit Abhiyan PEDIA (One of the Most Followed / Recommended) for UPSC Revisions: Click Here
IAS Abhiyan is now on Telegram: Click on the Below link to Join our Channels to stay Updated
IAS Abhiyan Official: Click Here to Join
For UPSC Mains Value Edition (Facts, Quotes, Best Practices, Case Studies): Click Here to Join
